Emission Sources Included
Ideally, to control carbon emission using a price on carbon, all emission sources should be included.
Emission Sources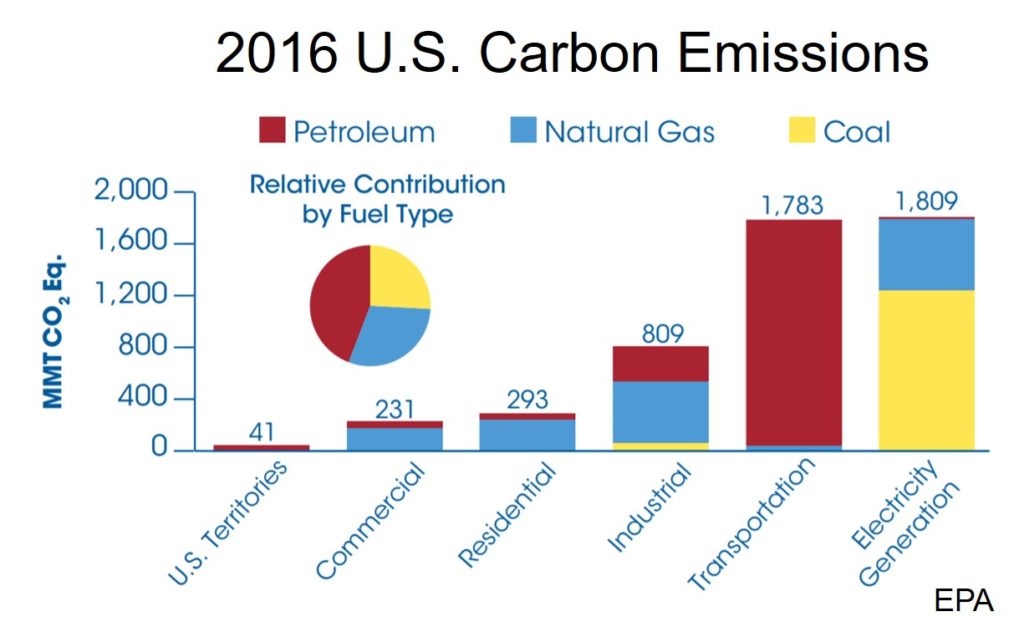
The primary emission sources in the U.S. in 2016 as plotted by the EPA are shown in the illustration on the right. The three primary sources are electricity generation, transportation and industrial. Buildings, which account for a lot of emissions use mostly electricity, so most are in the Electricity Generation category.
Click on figure to enlarge.
Emissions Covered
Carbon pricing can apply to a variety of emission sources. Some pricing systems, like the Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative (RGGI), in effect in nine northeastern U.S. states, is only on power generation which covers about 20% of total emissions; by contrast, the California cap and trade, extended in 2015 to include transportation, now covers about 85% of emissions. Most global pricing systems include power generation and industrial, but only a few include transportation (California, Quebec, New Zealand, Kazakhstan, and Shanghai). Percentage of emissions covered by a carbon pricing scheme in each geographic entity is shown below. The figure is from the World Bank.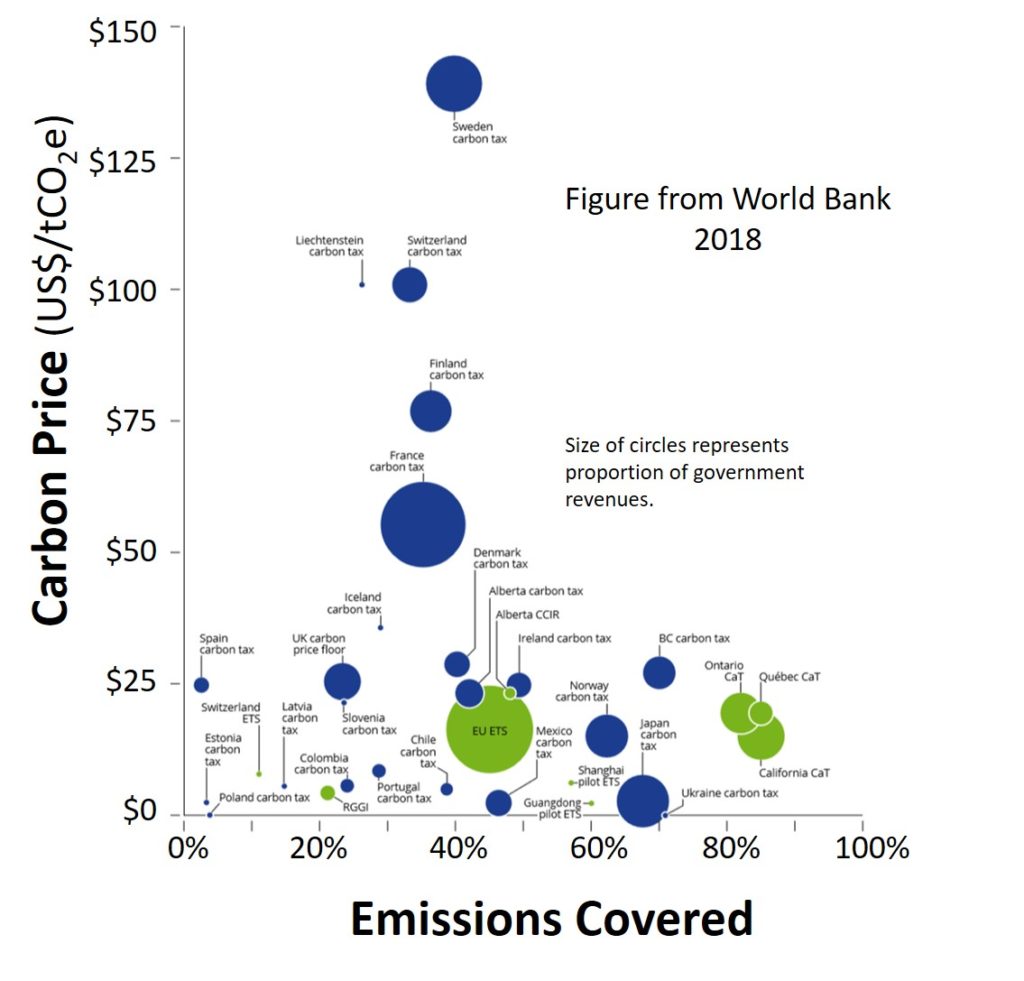
Click on figure to enlarge.
Most pricing systems cover in the range of 30-40% of emissions where they apply. To be most effective in modifying behaviors and business, the proportion of emissions covered needs to be much closer to 100%.
Last updated August 16, 2018